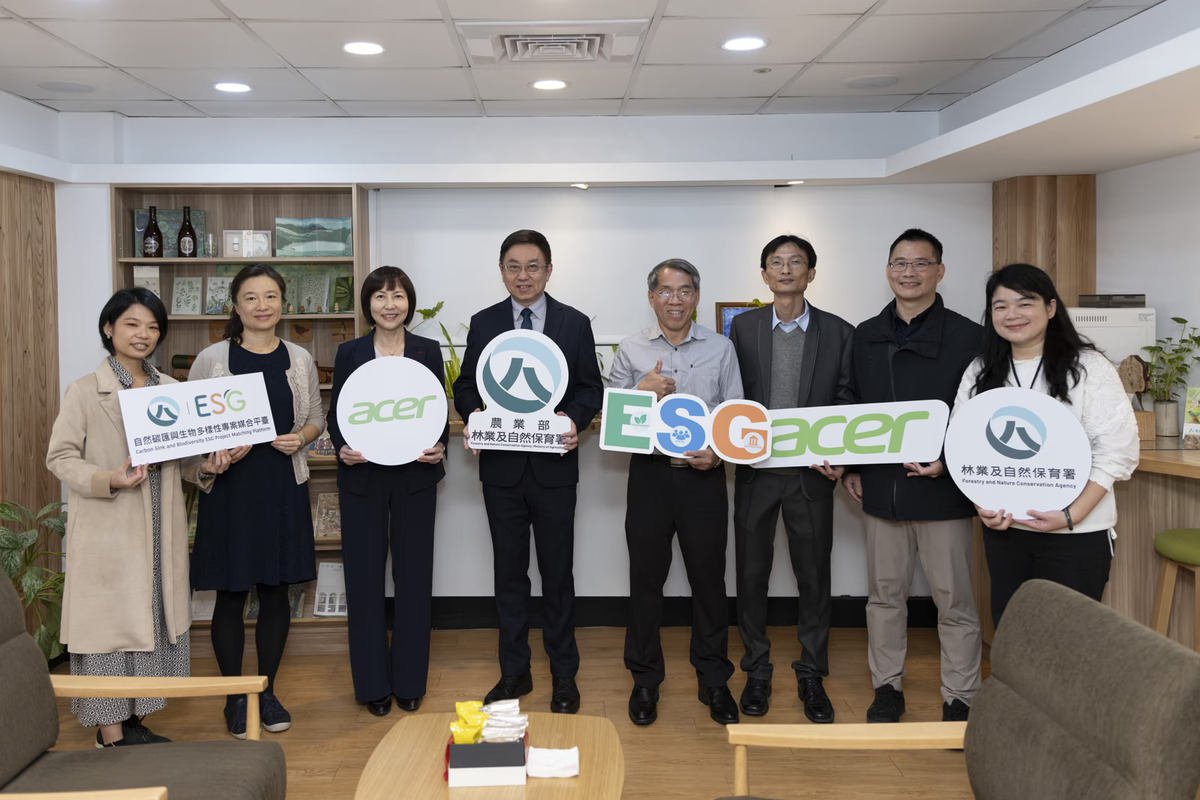
Acer has introduced its “Forest Neighborhood Coexistence” project in partnership with Taiwan’s Forestry and Nature Conservation Administration to support biodiversity surveys and environmental education in Dajianshan, Xizhi. The initiative focuses on ecological investigation, habitat restoration, and community-based learning around the forests near Acer’s headquarters. Working with National Taiwan Normal University’s TNFD research team, Acer helped carry out a baseline ecological survey using infrared cameras and nighttime fieldwork to document wildlife activity from Dajianshan to Sifenwei. Observed species include the Taiwan endemic giant red flying squirrel, ferret badger, pangolin, yellow-rumped scops owl, civet cat, and other mammals, birds, and reptiles.
The survey provides data to explore long-term monitoring of species in urban-adjacent foothills, addressing current gaps in ecological information for the region. Alongside scientific research, the project involves workshops, community discussions, and employee participation in habitat-related activities such as making nest boxes. Acer is also collaborating with local associations to integrate community knowledge into ecological records. The initiative aligns with UN SDG 15 and supports the aims of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework by advancing ecological study and restoration work in non-statutory protected areas.
















Leave a comment