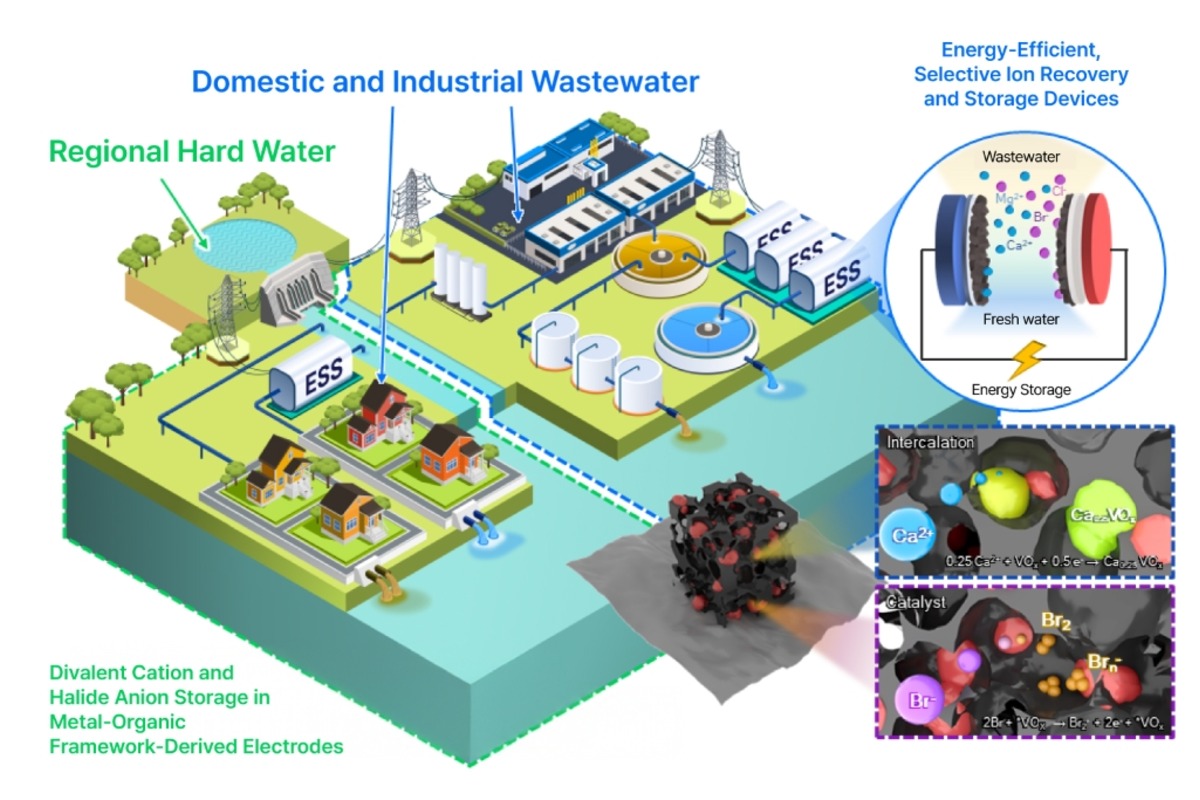
Samsung Electronics and Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU) have co-published a study in the journal Joule introducing a next-generation electrochemical water treatment technology capable of recovering and supplying power to external devices. The research, titled “Divalent and Halide Dual-Ion Storage of a Redox-Active Symmetric Cell for an Efficient Wastewater-Energy Nexus,” presents a system that integrates water purification with energy storage, addressing the high power consumption and cost challenges of conventional electrochemical methods.
The new approach eliminates the need for ion exchange membranes by using a metal oxide-based nanostructured electrode that allows ions to be stored and released through direct electron exchange. This innovation improves ion storage capacity by 200 percent and enhances storage rate by 20 percent compared to existing technologies. The process also enables spontaneous electrode regeneration without additional power input, reducing operational energy requirements by about half.
Developed through close collaboration between Samsung Research’s Life Solution Team and SKKU’s Department of Chemical Engineering, the technology offers potential applications in household and industrial systems. It could power water-related appliances while purifying water, paving the way for multifunctional energy-efficient environmental solutions. Samsung aims to continue advancing research partnerships to support sustainable technology innovation.















Leave a comment